关于如何进行EUS引导的胆道引流恶性梗阻性黄疸的多机构共识
时间:2019-01-19
作者:翻译:王君俊 审校:
点击: 次
关于如何进行EUS引导的胆道引流恶性梗阻性黄疸的多机构共识
背景与目的:EUS引导下胆道引流术(EUS-BD)在治疗恶性胆道梗阻(MBO)中有重要作用。然而,对于如何执行EUS-BD缺乏共识。
方法:在2018年2月对欧盟国际学会成员进行全球性多机构调查。调查由10个与EUS-BD相关的实践问题组成。
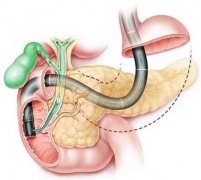
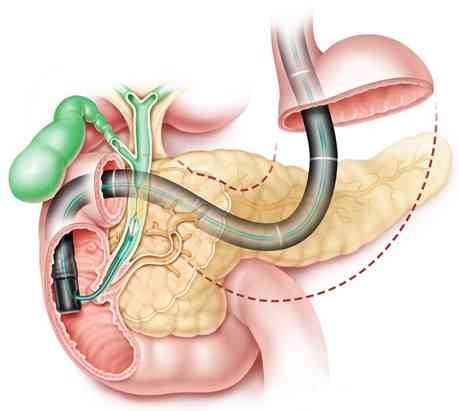
结果:46名内镜师完成了调查。大多数内镜师认为,EUS-BD可替代ERCP失败后的经皮肝穿刺胆道引流。在所有的EUS-BD方法中,支架会师技术是首选。自膨胀金属支架(SEMS)被大多数内窥镜专家所推荐。对于EUS引导下肝管-胃吻合术(HGS),部分覆膜SEMS是否优于完全覆膜SEMS的意见并不一致。推荐使用6-Fr的囊肿切开刀。在HGS方法中,推荐使用较长的SEMS(8或10cm)。在胆总管-十二指肠吻合术时,建议使用6cm的SEMS。推荐3段肝内胆管作为肝内入路途径。
结论:这是首次对世界范围内因恶性胆道梗阻实施EUS-BD的实践调查。因操作实践存在着广泛的差异,迫切需要随机研究来对此种治疗方式建立指导方案。
A multi-institution consensus on how to perform EUS-guided biliary drainage for malignant biliary obstruction.
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES:EUS-guided biliary drainage (EUS-BD) was shown to be useful for malignant biliary obstruction (MBO). However, there is lack of consensus on how EUS-BD should be performed.
METHODS:This was a worldwide multi-institutional survey among members of the International Society of EUS conducted in February 2018. The survey consisted of 10 questions related to the practice of EUS-BD.
RESULTS:Forty-six endoscopists of them completed the survey. The majority of endoscopists felt that EUS-BD could replace percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage after failure of ERCP. Among all EUS-BD methods, the rendezvous stenting technique should be the first choice. Self-expandable metal stents (SEMSs) were recommended by most endoscopists. For EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy (HGS), superiority of partially-covered SEMS over fully-covered SEMS was not in agreement. 6-Fr cystotomes were recommended for fistula creation. During the HGS approach, longer SEMS (8 or 10 cm) was recommended. During the choledochoduodenostomy approach, 6-cm SEMS was recommended. During the intrahepatic (IH) approach, the IH segment 3 was recommended.
CONCLUSION:This is the first worldwide survey on the practice of EUS-BD for MBO. There were wide variations in practice, and randomized studies are urgently needed to establish the best approach for the management of this condition.
翻译:王君俊 审校:张立超、侯森林