 超声内镜引导下胃造口辅助ERCP与小肠镜辅助ERCP对Roux-en-Y旁路吻合病人的一项国际化多中心对比试验
超声内镜引导下胃造口辅助ERCP与小肠镜辅助ERCP对Roux-en-Y旁路吻合病人的一项国际化多中心对比试验
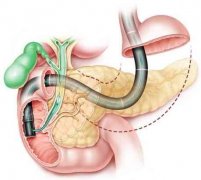
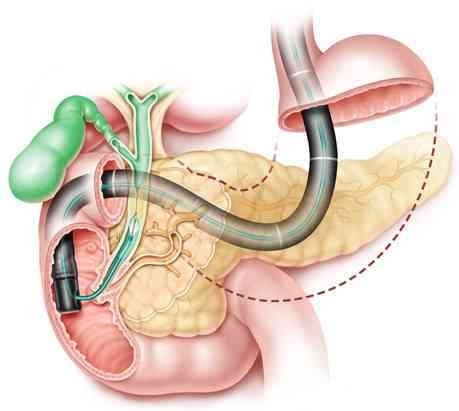
背景和目的:对Roux-en-Y旁路吻合(RYGB)的病人施行ERCP具有挑战性。超声引导下胃胃吻合术是一项有价值的新型技术,能进入旷置的胃以便容易施行传统的ERCP。我们的目的旨在于对比超声内镜引导下胃胃吻合术辅助ERCP(EUS-GG-ERCP)与肠镜辅助ERCP(e-ERCP) 在Roux-en-Y旁路吻合病人中操作结果和不良事件。
方法:纳入了5个三级中心在2014年至2016年期间接受了EUS-GG-ERCP或e-ERCP的RYGB患者。主要统计指标是ERCP的技术成功,其标准是根据预期对所选择的胆管成功插管。次要统计指标是(1)总操作时间(在EUS-GG组中,全部时间包括EUS-GG及ERCP时间之和)(2)住院时间(3)根据ASGE指南相关不良事件的发生率/严重程度。
结果:总共60位患者(平均年龄57.2±13.2, 75% 女性),其中30位(50%)患者接受EUS-GG-ERCP,30位(50%)患者接受 e-ERCP。 EUS-GG-ERCP 对比 e-ERCP 组有较高的技术成功率((100% vs 60.0%, p <0.001)。EUS-GG-ERCP 组的总共操作时间显著短于e-ERCP 组(49.8 分钟 vs 90.7 分钟, p<0.001)。EUS-GG组术后住院时间中位数较短(1 vs 10.5天,p = 0.02)。不良事件的发生率两组相近(10% vs 6.7%, p=1)。
结论:对于RYGB的患者EUS-GG-ERCP拥有高技术成功率和较短的操作时间,其可能优于e-ERCP,并且二者安全性无差异。
An international, multicenter, comparative trial of EUS-guidedgastrogastrostomy-assisted ERCP versus enteroscopy-assisted ERCP in patients with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass anatomy
Bukhari M;Kowalski T;Nieto J;Kunda R;Ahuja NK;Irani S;Shah A;Loren D;Brewer O;Sanaei O;Fayad L;Chen YI;Ngamruengphong S;Kumbhari V;Singh V;Aridi HD;Khashab MA;
BACKGROUND & AIMS: ERCP is challenging in patients with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) anatomy. EUS-guided gastrogastrostomy (GG) creation is a promising novel technique to access the excluded stomach in order to facilitate conventional ERCP. We aimed to compare procedural outcomes and adverse events (AEs) between EUS-guided gastrogastrostomy-assisted ERCP (EUS-GG-ERCP) and enteroscopy assisted ERCP (e-ERCP) in patients with RYGB.
METHODS:Patients with RYGB anatomy who underwent EUS-GG-ERCP or e-ERCP between 2014 and 2016 at 5 tertiary centers were included. The primary outcome was technical success of ERCP, defined as successful cannulation of the selected duct with successful intervention as intended.Secondary outcomes included (1) total procedural time (in the EUS-GG group, total procedural time included EUS-GG creation plus ERCP procedure time); (2) length of hospital stay; and (3) rate/severity of AEs graded according to the ASGE lexicon.
RESULTS:A total of 60 patients (mean age 57.2 ±13.2, 75% female) were included, of whom 30 (50%) underwent EUS-GG-ERCP and 30 (50%) underwent e-ERCP (DBE-ERCP 19 and SBE-ERCP 11). The technical success rate was significantly higher in the EUS-GG-ERCP versus the e-ERCP group (100% vs 60.0%, p <0.001). Total procedure time was significantly shorter in patients who underwent EUS-GG-ERCP (49.8 min vs 90.7 min, p<0.001). Postprocedure median length of hospitalization was shorter in the EUS-GG group (1 vs 10.5 days, p=0.02). Rate of AEs was similar in both groups (10% vs 6.7%, p=1)。
CONCLUSION:EUS-GG-ERCP may be superior to e-ERCP in patients with RYGB anatomy in terms of a higher technical success and shorter procedural times and offers a similar safety profile.
翻译:王浩 审校:张立超、侯森林 (Gastrointestinal endoscopy 2018.)